THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY
THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY
It is a chromatographic separation method used to separate mixtures, to check the purity of a mixture, and to monitor the progress of the reaction.
Procedure
- A glass plate coated with a material of the adsorbent will constitute the stationary phase. The material is made into a slurry or a paste and the glass plate is coated with it by a thin layer applicator and dried.
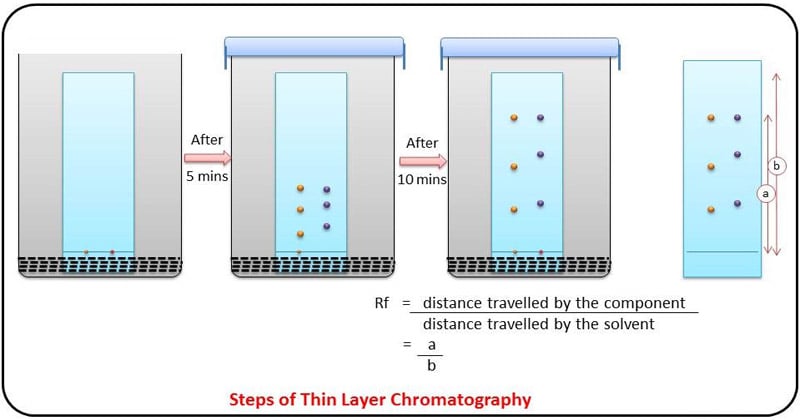
- This glass plate with a thin layer of stationary phase is called chromatoplate. The mixture to be separated is applied to one end of the plate and it is placed in the solvent.
- When the solvent reaches near the top, it is removed and dried. If the components are colored the spots can be readily located.
- If the components are colorless the dried plate is sprayed with a suitable reagent to make the spot colored.
- In this way, the position of the components is located and their Rf values are determined.
- Rf value is the ratio of the distance traveled by a component to the distance traveled by the solvent is known as the Retention factor.
- Under a given set of conditions, the Rf value is constant for a given component. Hence it is possible to identify the various components by determining their Rf values.
Advantages
- It can be used for the separation of minute quantities
- Sensitive and sharp separation is possible.
- Speed of separation is high.
- This method provides a wide choice of stationary phases.
Applications
- It is used for the detection of purity of any sample and the identification of compounds.
- It is used in the pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetic industries.
- It is used for biochemical analysis
Comments
Post a Comment