GLASS ELECTRODE
GLASS ELECTRODE
It is a secondary reference electrode that produces a constant and reproducible electrode potential.
It is an ion-selective electrode used with other reference electrodes to generate a potential difference.
Construction
It is made up of a special glass of relatively low melting point and high electrical conductivity, in the form of a sealed glass tube filled with 0.1M HCl, a platinum wire is inserted into it, to make electrical contact.
The glass electrode is represented as Pt| 0.1M HCl | Glass | H+
The H+ ion concentration inside the electrode is constant. When the electrode is immersed into a solution of unknown H+, it becomes sensitive to the outside concentration in the solution. Such a sensitivity arises because of the difference between the H+ ion concentration inside and outside. The electrode potential of the glass rod is : EG = EG0 + 0.0591 log [ H+ ]
EG = EG0 - 0.0591 pH
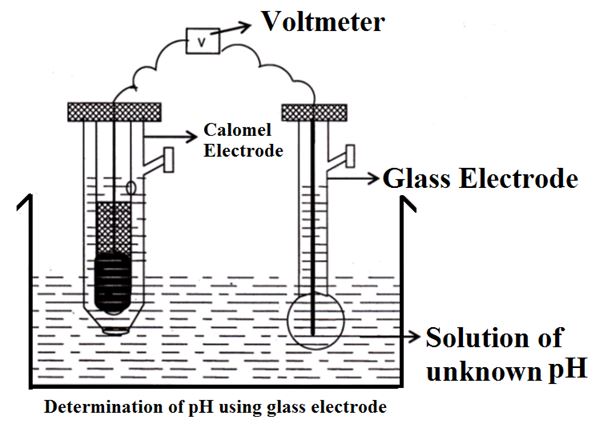
The glass electrode is used as the internal reference electrode for the determination of the pH of a solution.
When two solutions of different values are separated by a glass membrane, a difference in potential is developed which is proportional to the difference in pH value.
In order to determine the pH of a solution, the glass electrode is coupled with a saturated calomel electrode, the emf of the cell is determined.
Ecell = Ecalomel - Eglass
EGlass = EG0 – 0.0591 pH
Ecell = 0.2422 – [ EG0 - 0.0591 pH ]
Ecell = 0.2422 + 0.0591 pH - EG0
0.0591 pH = Ecell + EG0 – 0.2422
pH = Ecell + EG0 – 0.2422
0.0591
👍
ReplyDelete