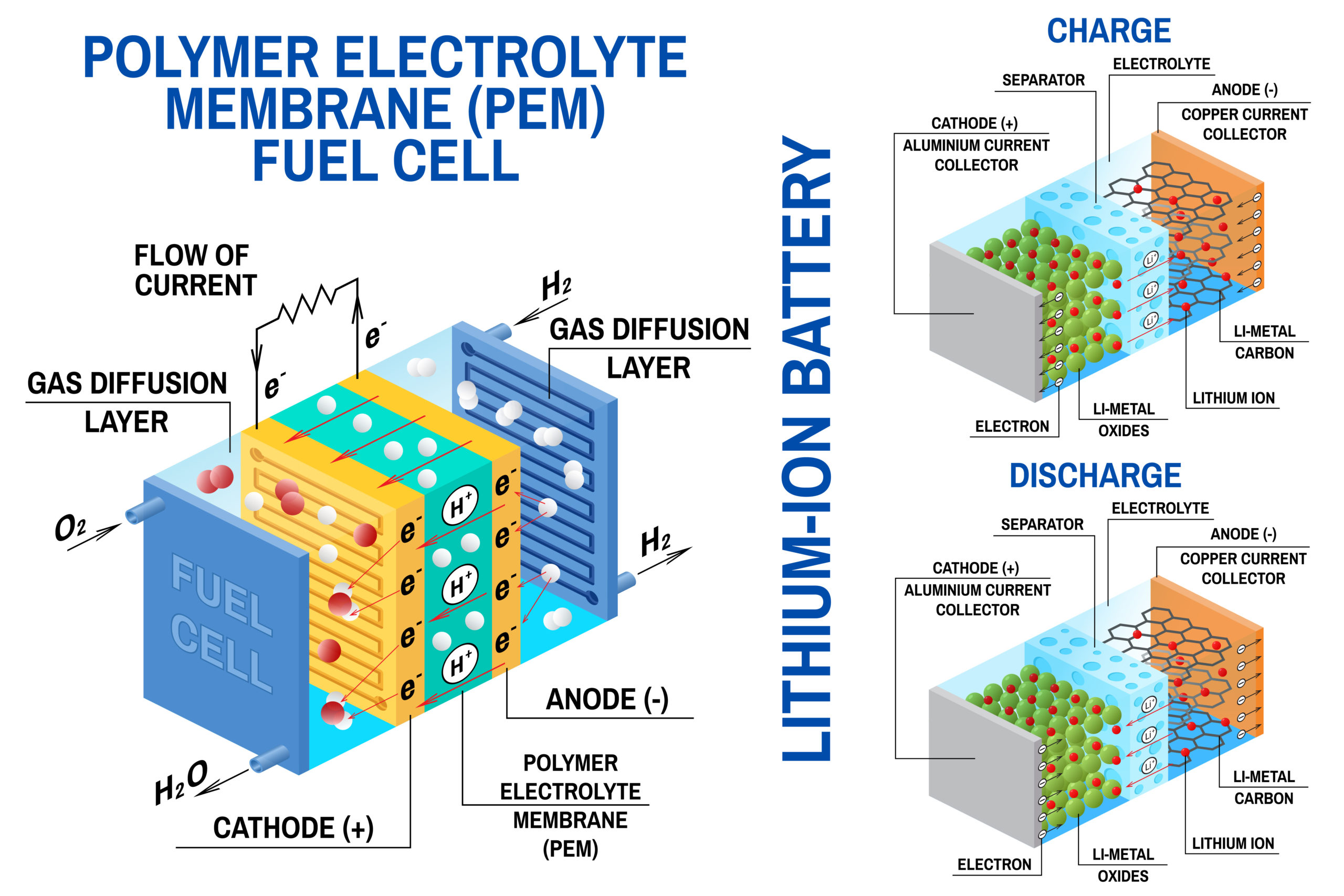
LITHIUM-ION BATTERY
LITHIUM-ION BATTERY
Lithium-ion batteries are secondary rechargeable batteries.
It has an emf that varies from 3.5-4V depending on electrode potential.
Construction
The 3 primary components of a lithium-ion battery are:
- The anode is lithiated graphite (graphite in which lithium ions are inserted in between the layer of carbon atoms.
- The cathode is a mixed metal oxide like LiCoO2, LiMnO2 or LiFeO2
- The electrolyte is a lithium salt (LiPF6, LiBF4, or LiClO4 ) in an organic solvent.
This is rechargeable. This is done by applying a higher voltage than the voltage of the battery, across the electrodes.
The lithium-ion moves from anode to cathode during discharging and from cathode to anode while charging.
Cell reaction
Anode : LixC6 ---> 6C + x Li+ + x e-
Cathode : Li1-x CoO2 + x Li+ + xe -----> LiCoO2
Overall cell reaction : LixC6 + Li1-x CoO2 -------> LiCoO2 +6C
Characteristics
- Depending on the choice of material for the anode, cathode, and electrolyte the voltage, capacity, life, and safety of a lithium-ion battery can change drastically.
- Li-ion batteries are charged not greater than 80 to 90 percent of their maximum state of charge and are not allowed to discharge below 30 percent, because operation at extremely high or low states of charge can reduce battery life.
- They are of different forms, common forms are cylindrical cells and prismatic cells
Comments
Post a Comment